Address
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 9:00 AM - 6:00 PM
Address
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 9:00 AM - 6:00 PM
India has been a global hub for manufacturing and technical jobs, with industries evolving due to advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and Industry 4.0. The future of these jobs is poised for transformation, driven by technology, government policies, and global trends. Additionally, the rise of digital manufacturing, smart supply chains, and sustainable production practices are further reshaping employment dynamics in this sector. The convergence of traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technologies is expected to create a hybrid workforce that blends human expertise with AI-driven automation.
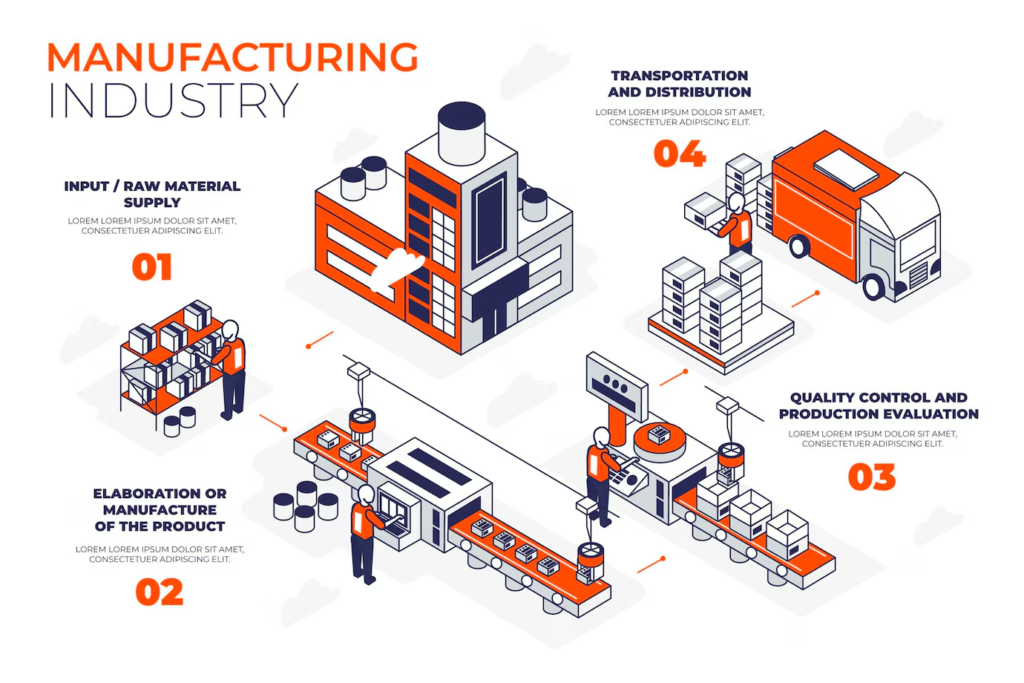
This blog explores the significant factors shaping the future of manufacturing and technical employment in India, focusing on technological advancements, industry shifts, and workforce adaptations.
Industry 4.0, characterized by the integration of IoT, AI, robotics, and data analytics, is reshaping India’s manufacturing sector. With smart factories becoming a reality, there is an increasing need for skilled professionals who can operate, maintain, and develop these systems.
Companies are leveraging digital twins, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring to enhance efficiency. While automation will replace some manual jobs, it will also create new roles such as AI specialists, robotics engineers, and cybersecurity experts. The challenge for India lies in upskilling the existing workforce and preparing future professionals to meet the demands of smart manufacturing.
Additionally, the government’s push for digital transformation through initiatives like the National Policy on Electronics and Make in India is accelerating the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. Indian manufacturers are increasingly investing in AI-driven production lines and smart logistics, leading to a demand surge for technical talent adept at handling these systems. The success of Industry 4.0 in India will depend on how effectively the workforce transitions from traditional labor-intensive methods to technology-driven production processes.
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is revolutionizing India’s automotive and manufacturing landscape. With the government’s aggressive push towards EV adoption, including policies like FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles), the demand for skilled workers in battery technology, EV assembly, and power electronics is on the rise.
EV production requires expertise in areas such as battery management systems, embedded software, and sustainable materials. Additionally, green manufacturing practices are becoming essential as industries shift towards sustainability and eco-friendly production methods. Companies are adopting renewable energy sources, reducing carbon footprints, and implementing energy-efficient processes to align with global environmental standards.
As India aims to become a key player in EV manufacturing, job opportunities in this sector will expand significantly. The need for mechanical engineers, software developers, and materials scientists specializing in sustainable solutions will grow. Training programs and government-industry collaborations will be crucial in ensuring that India’s workforce is prepared for this green revolution.
Automation and robotics are reshaping manufacturing by improving efficiency, precision, and scalability. Indian industries are increasingly deploying robotic process automation (RPA) and collaborative robots (cobots) to streamline production processes and reduce human errors.
While automation may lead to job displacement in repetitive tasks, it also creates opportunities in robotics maintenance, AI programming, and system integration. The demand for professionals skilled in mechatronics, industrial automation, and AI-driven robotics is expected to grow.
Moreover, the adoption of automation extends beyond manufacturing to logistics, warehousing, and quality control. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs), drone-based inspections, and AI-driven supply chain management are becoming the norm. To stay competitive, Indian workers must transition from traditional manufacturing roles to technical positions requiring expertise in machine learning, robotics programming, and predictive analytics.
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is revolutionizing industries by enabling on-demand production, reducing waste, and enhancing design flexibility. Sectors such as aerospace, healthcare, and automotive are leveraging 3D printing for rapid prototyping and customized production.
India’s adoption of 3D printing is still in its early stages, but the potential is enormous. As companies invest in advanced printing technologies, job roles in 3D design, material science, and process optimization will emerge. Engineers skilled in computer-aided design (CAD), material formulation, and digital manufacturing will be in high demand.
Educational institutions and vocational training centers are increasingly offering specialized courses in additive manufacturing. Government initiatives promoting Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat (Self-Reliant India) are further driving investments in this sector. For India to compete globally, a robust ecosystem of research, development, and skilled talent in 3D printing will be crucial.
The rapid technological advancements in manufacturing demand a workforce that is continuously learning and adapting. Traditional technical skills are no longer sufficient, and reskilling/upskilling programs are becoming a necessity.
India’s educational institutions, in collaboration with industries, must develop specialized courses focusing on AI, IoT, cybersecurity, and automation. Online learning platforms and government-led initiatives like Skill India are playing a crucial role in bridging the skill gap.
Companies are also investing in internal training programs to equip their employees with the necessary digital competencies. The future workforce needs to be agile, technologically proficient, and capable of working in an environment where human-machine collaboration is the norm. Encouraging a culture of continuous learning and professional development will be key to ensuring India remains a global manufacturing powerhouse.
The Indian government is playing a vital role in shaping the future of manufacturing and technical jobs. Policies such as Make in India, Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, and Digital India are driving investments in technology and infrastructure.
Tax incentives, grants, and subsidies are encouraging industries to adopt advanced manufacturing technologies. Additionally, initiatives such as National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) and sector-specific training programs are helping create a workforce ready for the future.
Public-private partnerships (PPP) are fostering innovation, research, and development in manufacturing. As the government continues to emphasize self-reliance and indigenous production, job creation in technical fields will rise. A well-defined policy framework and industry collaboration will ensure India’s manufacturing sector remains competitive on a global scale.
The future of manufacturing and technical jobs in India is undergoing a paradigm shift. Technological advancements, sustainability initiatives, and policy support are driving transformation across industries. While automation may replace some jobs, it is also creating new opportunities that require advanced technical skills.
To stay ahead, India must focus on reskilling its workforce, embracing smart manufacturing, and leveraging government policies for growth. The transition towards a technology-driven manufacturing sector will determine India’s global competitiveness in the coming years.
NOTE:- For more JOBS, visit Daily Liv India.
Images sourced from Freepik.